4.1 AED Use in Clinical Settings
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) are crucial for early defibrillation in cardiac arrest. As a healthcare provider, you will frequently encounter AEDs in hospitals, clinics, ambulances, and public settings.
Key Differences in HCP AED Use
- Immediate recognition of shockable rhythms (though AED analyzes for you)
- Integrating AED use with ongoing CPR
- Special considerations in clinical settings (e.g., pacemakers, medication patches, wet patients)
Steps for Using an AED
1. Power On the AED
- Some AEDs turn on automatically when opened, while others require a button press.
2. Attach the AED Pads
- Expose the patient’s chest (shave if necessary).
-
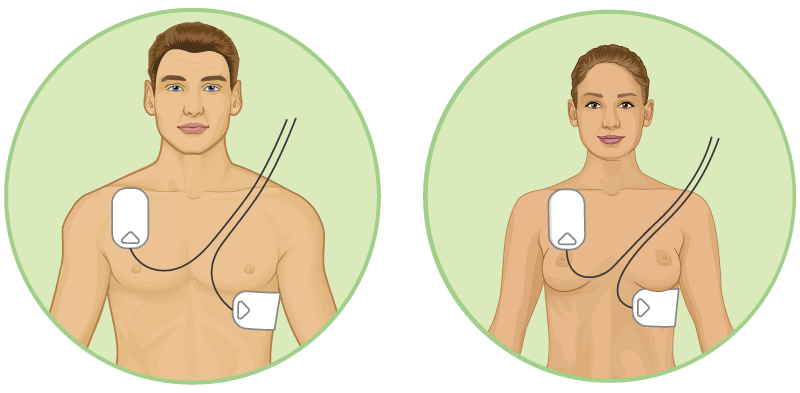
Place pads in anterolateral position:
×Place pads in anterolateral position:
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved- Right pad: Below the right clavicle (collarbone).
- Left pad: Side of the chest, below the left nipple.
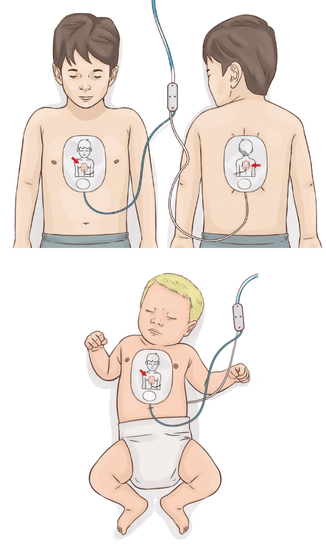
- If using
anterior-posterior placement
(common in infants/small children):×anterior-posterior placement
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved- Front pad: Center of chest.
- Back pad: Between shoulder blades.
3. Analyze the Rhythm
- Ensure no one is touching the patient.
- Press the analyze button if prompted (some AEDs analyze automatically).
4. Deliver the Shock if Advised
- Clear the area and loudly announce: “CLEAR!”
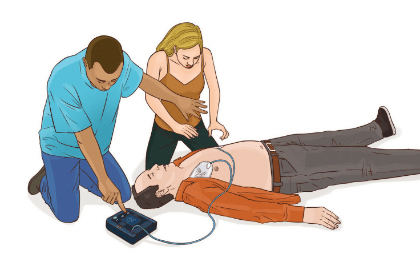
- Ensure
no one is touching the patient
.×no one is touching the patient
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved - Press the shock button if required (some AEDs shock automatically).
5. Resume CPR Immediately
- Do not check for a pulse yet—immediately start compressions.
- Continue CPR for 2 minutes before the next analysis.
Special Considerations in Clinical Settings
1. Pacemakers and Implanted Defibrillators
- Avoid placing AED pads directly over a pacemaker or defibrillator (usually seen as a lump under the skin).
- Place pads at least 1 inch away from the device.
2. Medication Patches
- If a medication patch (e.g., nitroglycerin patch) is present where the pad should go, remove it and wipe the skin dry.
3. Wet or Sweaty Patients
- Remove the patient from water before using an AED.
- If the patient is very sweaty, wipe the chest dry before attaching pads.
4. Hairy Chests
- Thick chest hair can prevent pads from making contact with the skin.
- Use a razor (if available) to quickly shave the area, or apply one set of pads, rip them off to remove hair, and apply a fresh set.
Integrating AED Use with CPR
Unlike layperson CPR, healthcare providers must integrate AED use without interrupting compressions. Every second counts—maximize hands-on time to improve survival rates!