4.1 Pediatric BLS Overview
Definition of a Child or Infant
The American Heart Association (AHA) defines a child as anyone from about 1 year of age to the onset of puberty, typically marked by secondary sex characteristics. An infant is a child under 1 year old, excluding newborns in the first few hours after birth.
Initial Assessment & Response
Pediatric BLS begins with a structured assessment and immediate action. The following steps apply to a single rescuer:
Single Rescuer Pediatric BLS
- Verify Scene Safety: Ensure the area is safe for both you and the victim.
- Check for Responsiveness:
- Child: Tap the shoulder and shout, “Are you okay?”
- Infant: Tap the bottom of the foot and shout, “Are you okay?”
- Call for Help: If the victim is unresponsive, shout for assistance.
- Activate the Emergency Response System (ERS): Call 911 or mobilize an ALS team if available.
- Retrieve AED and Emergency Equipment: If available, retrieve the AED and emergency supplies or send someone to do so.
Breathing and Pulse Assessment
Scan the Chest
Before checking for a pulse, observe the chest to assess whether the child or infant is breathing normally. Look for consistent rise and fall, which indicates effective ventilation.
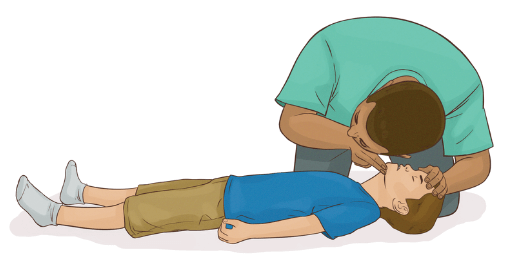
Child: Chest Rise & Fall
×
Child: Chest Rise & Fall
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
×

Child: Chest Rise & Fall

© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
- Position yourself at eye level with the child's chest.
- Look for visible rise and fall of the chest, which indicates normal breathing.
- Observe for no more than 10 seconds.
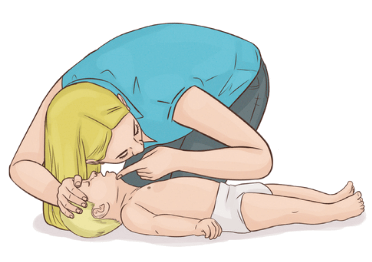
Infant: Chest Rise & Fall
×
Infant: Chest Rise & Fall
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
×

Infant: Chest Rise & Fall

© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
- Watch the infant’s entire torso, as movement may be subtle.
- Gasping or irregular breathing is not considered normal.
- If there is no normal breathing and no pulse after 10 seconds, begin CPR immediately.
Locating the Pulse
Child: Carotid Pulse
×
Child: Carotid Pulse
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
×

Child: Carotid Pulse

© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
- Use two or three fingers to locate the trachea on the side of the neck.
- Slide into the groove between the trachea and neck muscles to feel for the carotid pulse.
- Feel for at least 5 seconds, but no more than 10 seconds.
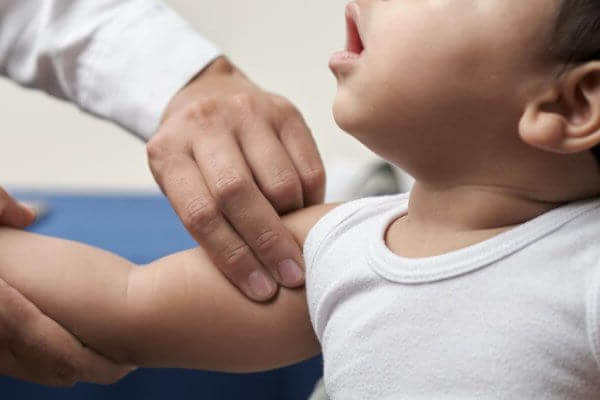
Infant: Brachial Pulse
×
Infant: Brachial Pulse
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
×

Infant: Brachial Pulse

© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
- Place two fingers on the inside of the upper arm, between the elbow and shoulder.
- Press gently to feel for the brachial pulse.
- Feel for at least 5 seconds, but no more than 10 seconds.
When to Begin CPR
If the victim is unresponsive, not breathing, and has no pulse, begin CPR immediately, starting with chest compressions.
CPR Approach: Lay Rescuers vs. Healthcare Providers
| Condition | Action for Lay Rescuers | Action for Healthcare Providers |
|---|---|---|
| No normal breathing, no pulse | Hands-only CPR (compressions only) | Full CPR (30:2 for single rescuer, 15:2 for two rescuers) |
| No normal breathing, pulse present | Monitor the victim until help arrives | Rescue breathing (covered in Section 4.3) |
| Normal breathing, pulse present | Stay with the victim and monitor | Stay with the victim and monitor |
Important Notes
- Hands-only CPR is acceptable for lay rescuers who are untrained or unwilling to give rescue breaths.
- Healthcare providers should perform full CPR, including ventilations, unless an advanced airway is in place.