3.1 Adult BLS Overview
Definition of an Adult
The American Heart Association (AHA) defines adult CPR as appropriate for individuals over the age of 8 years or post-adolescence. This is typically indicated by secondary sex characteristics, such as chest or underarm hair in males and breast development in females.
Initial Assessment & Response
Adult BLS begins with a structured assessment and immediate action. The following sequence should be followed by a single rescuer:
Single Rescuer Adult BLS
- Verify Scene Safety: Ensure the area is safe for both you and the victim.
- Check for Responsiveness: Tap the victim’s shoulder and shout, “Are you okay?”
- Call for Help: If the victim is unresponsive, shout for nearby assistance.
- Activate the Emergency Response System (ERS): Call 911 or mobilize an Advanced Life Support (ALS) team if available.
- Retrieve AED and Emergency Equipment: If available, retrieve the Automated External Defibrillator (AED) and necessary emergency supplies or assign someone else to do so.
Breathing and Pulse Assessment
- Look for chest rise and fall for no more than 10 seconds.
- If the victim is not breathing normally, they may be in cardiac arrest.
- Check for a carotid pulse. If a pulse is not detected within 10 seconds, begin CPR immediately.
Locating the Carotid Pulse
×
Locating the Carotid Pulse
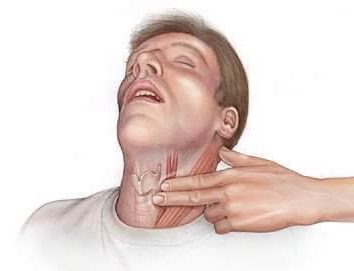 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
- Locate the trachea using two or three fingers.
- Slide your fingers into the groove between the trachea and the neck muscles to feel for the carotid pulse.
- Feel for at least 5 seconds but no more than 10 seconds. If no pulse is detected, begin CPR.
When to Begin CPR
If the victim is unresponsive, not breathing, and has no pulse, begin CPR immediately starting with chest compressions.
CPR Approach: Lay Rescuers vs. Healthcare Providers
| Condition | Action for Lay Rescuers | Action for Healthcare Providers |
|---|---|---|
| No normal breathing, no pulse | Hands-only CPR (compressions only) | Full CPR (30:2 compressions-to-breaths) |
| No normal breathing, pulse present | Monitor the victim until help arrives | Rescue breathing (covered in Section 3.4) |
| Normal breathing, pulse present | Stay with the victim and monitor | Stay with the victim and monitor |
Important Notes
- Hands-only CPR (chest compressions only) is recommended for lay rescuers who are untrained or unwilling to provide rescue breaths.
- Healthcare providers should perform full CPR, including compressions and rescue breaths, unless an advanced airway is in place.