3.4 B – Rescue Breathing
What Is Rescue Breathing?
Rescue breathing is the act of providing assisted ventilations to an unresponsive adult victim who has a pulse but is not breathing or not breathing normally (e.g., only gasping).
Methods of Rescue Breathing
Rescue breaths can be provided using one of the following techniques:
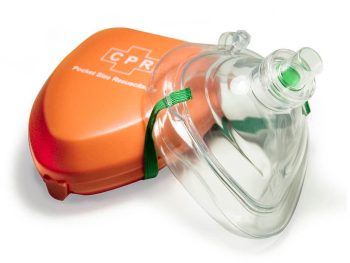
- A
barrier device
(e.g., face shield or pocket mask)×barrier device
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved - A
bag-mask device
, if trained and available×bag-mask device
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved - Mouth-to-mouth, if no other equipment is accessible
Rescue Breathing Guidelines for Adults
- Deliver 1 breath every 5–6 seconds (approximately 10–12 breaths per minute)
- Each breath should last 1 second and produce visible chest rise
- Avoid excessive ventilation — do not overinflate the lungs
- Recheck the victim’s pulse approximately every 2 minutes
Emergency Response & Naloxone Use
Ensure that the Emergency Response System (ERS) has been activated. If an opioid overdose is suspected, administer naloxone if available and trained to do so. Continue rescue breathing until normal breathing resumes or help arrives.
When to Switch to Full CPR
If the victim loses their pulse at any point, begin full CPR immediately using a 30:2 compression-to-breath ratio. Continue until:
- EMS or an Advanced Life Support (ALS) team arrives
- The victim shows clear signs of life (e.g., normal breathing, purposeful movement, pulse returns)
- Another trained provider takes over
- You are too exhausted to continue safely
Pulse & Breathing Decision Matrix
| Pulse | Breathing | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Absent | Not normal | Start full CPR immediately (30:2 ratio) |
| Present | Not normal | Begin rescue breathing (1 breath every 5–6 seconds) |
| Present | Normal | Monitor and wait for EMS |