PEDIATRIC BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (BLS)
Definition:
AHA guidelines define a “child” as from about 1 year of age to the onset of adolescence as defined by the presence of secondary sex characteristics (puberty). An “infant” is under 1 year of age, except for neonatal victims such as newborns in the first hours after birth.
Single Rescuer BLS
- verify that the scene is safe for rescuer and victim
- Check for responsiveness. Tap the child’s shoulder or the bottom of the infant’s foot and shout “are you ok?”
- if the victim is not responsive, shout for nearby help and activate Emergency Response System (for example, call 911 or mobilize Advanced Life Support team)
Scan the victim’s chest for rise and fall for no more than 10 seconds. It may be difficult to detect pulse in a small-bodied victim so if pulse is not detected for 10 seconds, start CPR.
Check for pulse in child victim by palpating a carotid pulse:
- locate the trachea using 2 or 3 fingers
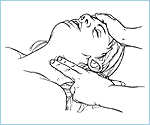
- slide fingers into the groove between the trachea and the muscles at the side of the neck, where you can feel the carotid pulse
- feel the pulse for no less than 5 but no more than 10 seconds. If you do not definitely feel a pulse begin CPR
Check for pulse in infant victim by palpating a brachial artery pulse: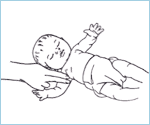
- place 2 fingers on the inside of the upper arm, midway between the elbow and shoulder
- press the fingers to attempt to feel the pulse for at least 5 but no more than 10 seconds
If the victim is not breathing normally but a pulse is present, provide rescue breathing:
“Rescue breathing” is giving assisted breaths to an unresponsive victim who has a pulse but is not breathing. This can be done safely with a barrier device or bag-mask, or mouth to mouth if none available. Rescue breaths for infants and children are given at a rate of 1 breath every 3-5 seconds, or about 12 to 20 breaths per minute)
- give each breath in 1 second
- each breath should result in visible chest rise
- check the pulse about every 2 minutes
If the victim is not breathing and no pulse is detected, begin CPR.