Choking is usually caused by a piece of foreign matter such as food becoming lodged in a person’s windpipe. Because a choking victim is fully aware that he cannot breathe normally, a sense of panic may overcome them, making assessing the situation and rescue efforts difficult. It’s important to try and keep the victim calm in order to determine whether your assistance is truly necessary or if the victim’s own coughing reflex is sufficient.

Start by asking the person if he is choking. This simple step can be deceptively effective – the victim may be coughing violently or even gasping for air, but if he is able to answer then he is probably not choking. A choking victim will not be able to speak since oxygen cannot reach his lungs. But if after asking the person if he’s choking all he can do is gesture or point to his throat and you notice his face starting to turn blue, then he is most likely choking and you will need to perform the Heimlich Maneuver immediately.
- Start by finding the proper stance – behind the victim with one of your feet approximately between the victim’s feet.
- Wrap one of your arms around the victim and place your hand in a closed fist just above his belly button.
- Place your other hand directly on top of the first.
- Squeeze the victim’s abdomen in quick upward thrusts as many times as it is necessary to dislodge the object in his windpipe.
Choking Rescue Procedure for infants
Similarly to adults, if an infant victim can cough or make sounds, you should allow him to try to dislodge the foreign matter on his own. If it appears that the infant is unable to breathe and is not coughing, crying or making any sound, do NOT leave the infant alone and dial 9-1-1 immediately.
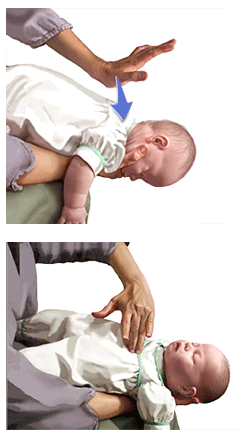
Unlike for adult or older children victims, the Heimlich maneuver is not performed on a choking infant. Instead, the following steps should be performed if the infant is not breathing or is clearly struggling to breathe:
- Holding the infant securely, place him faced down on your forearm so that his head is lower than his chest.
- Support his head in the palm of your hand against your thigh or lap and ensure that you don’t cover his mouth or twist his neck.
- With the heel of your free hand give up to 5 firm back slaps between his shoulder blades.
- While still keeping his head lower than his body, turn him face up and look inside his mouth to see if the blockage had dislodged.
- If you can see the object and can safely remove it, do so – but do NOT stick your finger(s) into the infant’s throat to feel for blockage, as this may push it deeper into his windpipe.
- If the airway is still blocked (the infant is not breathing or crying), place 2 fingers on his breastbone just below the nipple line and give 5 quick chest thrusts.
- Again, check if the airway was cleared or if the infant begins to breathe on his own or to cry. If not, continue to perform 3 cycles of 5 back slaps and 5 chest thrusts, or until the object comes out, whichever comes first.
- If the infant is still not breathing, and you haven’t done so already, dial 9-1-1 to summon EMS and for assistance.
Once you are successful in getting the object out of the airway, the infant will be in distress and weak, and will need to be closely monitored. If you observe signs of weak breathing or the infant is experiencing difficulty swallowing, you should seek immediate medical help.
Breaks in the skin range from pin punctures or minor scratches to extensive cuts, tears and gashes. In First Aid, open wounds are divided into six categories: abrasions, amputations, avulsions, incisions, lacerations, and punctures. 
Abrasions are caused by rubbing or scraping with the wound generally shallow and a portion of the skin damaged, leaving a raw surface with minor bleeding.
Amputations involve extremities such as fingers, toes, hands, feet, or entire limbs severed completely from the victim’s body. Depending on the type of amputation, bleeding may be excessive or very restricted.
Avulsions are injuries that tear a whole piece of skin and tissue from the body, usually as a result of violent or forcible separation. Although these injuries may often be successfully repaired if treated quickly, there is great danger of infection and bleeding.
Incisions are produced by a sharp cutting edge such as a knife or glass. If an incision is deep, major blood vessels and nerves my be severed making it difficult to control blood flow.
Lacerations are similar to incisions but have rough or jagged edges with the flesh torn or cut with a blunt edge.
Puncture wounds are produced by pointed objects being forced through the skin. Although the small number of blood vessels damaged sometimes prevents excessive bleeding, there is danger of infection due to this poor drainage.
General First Aid for bleeding
The main objectives in administering first aid to a bleeding victim are to stop blood flow and to prevent germs from entering the wound.
- expose the wound by carefully cutting away at clothing around it
- carefully remove any loose foreign body around the wound with clean material, always wiping away from the wound
- if an object has impaled the victim, do not attempt to remove it as this may cause excessive bleeding and other serious injury
- dress the wound with sterile gauze or similar material, covering the wound completely
- unless otherwise specified, apply direct pressure to the wound to stem blood flow
- keep the victim still and calm
- if necessary, treat the victim for shock
- seek medical attention
Electricity travels through conductors – any material which allows electrical flow – as it tries to reach the ground. Because people make excellent conductors, minor electric shocks are a common household hazard. Fortunately it is usually more surprising than dangerous and does not require medical attention. However, some basic precautions should be taken to ensure that the shock does not interfere with the body’s normal electrical impulses including the functions of the brain and the heart. Prolonged exposure to a direct source of electricity can also cause severe burns to the skin and the tissue.
In the event of electrocution do not rush to assist the victim until you are certain that he is no longer in contact with electricity. Otherwise the current will pass through the victim directly to you.
- If at all possible, turn off the source of electricity (i.e. light switch, circuit breaker, etc.) If this is not an option, use non-conductive material such as plastic, glass, or dry wood to separate the source of electricity from the victim.
- If the injuries appear serious or extensive, dial 9-1-1.
- Check the victim’s vitals signs such as the depth of his breathing and regularity of his heart beat. If either one is affected by exposure to electricity or if the victim is unconscious, begin to perform CPR.
- Treat any areas of the victim’s body that may have sustained burns.
- If the victim is responsive and does not appear seriously injured but looks pale or faint, he may be at risk of going into shock. Gently lay him down with his head slightly lower than his chest and his feet elevated.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is a general cooling of the entire body and is caused by extensive exposure to extreme cold at which time the body fails to generate heat. Individuals experiencing fatigue, hunger, and poor physical condition are more likely to experience hypothermia and should take every possible precaution to avoid exposure to the elements.
First Aid treatment for a victim of hypothermia are:
- protect him from the elements as quickly as possible
- remove all wet clothing
- wrap the victim in blankets
- provide the victim with warm liquids to drink
- seek immediate medical attention
Frostbite
The signs of frostbite are not always apparent to the victim since the nature of this injury is its numbing effect of the affected area.
Treating frostbite consists of the following:
- apply loose sterile dressing to the injury
- have the victim drink warm fluids containing sugar
- do NOT rub the frostbitten area
- do NOT attempt to heat the area with heat lamps or hot water bottles
- do NOT place the victim near a stove, fire or radiator
- do NOT allow the victim to drink coffee as caffeine restricts blood flow
- seek immediate medical help
Heat Stroke
Heat stroke is a sudden onset of illness from extensive exposure to the sun or other sources of heat. The most important and damaging effect of heat stroke is the victim’s inability to produce sweat, causing the body temperature to rise uncontrollably.
The signs of heat stroke are:
- flushed, dry, very hot skin
- strong and rapid pulse which may become weak as the victim’s condition worsens
- irregular respiration followed by loss of consciousness
Failure to quickly lower the victim’s body temperature will result in brain damage or death. To treat the victim of heat stroke:
- move the victim to a cool environment
- remove all clothing
- wrap the victim in moist sheets or immerse him in cool water
- seek immediate medical attention
Black Eye is caused by broken blood vessels (or, bleeding beneath the skin) around the eye. Hyphema is when there is bleeding inside the eye (blood in the front chamber of the eye or the cornea). To treat, apply a cold pack or ice pack to reduce the swelling of the eye. If blood is visible in the eye or the victim complains of vision problems, seek medical attention.
Foreign objects in the eye can range from minor to severe. When assisting with removal of a foreign object from the eye, make sure your hands are clean. When examining, pull the lower lid down while the victim looks up, and vice versa in the opposite direction. Clean the eye with saline solution or clean water. If unable to remove the object or the victim’s vision worsens, call 911.
A chemical splash can cause blindness and must be treated immediately. If no eye-washing station is available, have the victim rinse the effected eye under running water for at least 20 minutes and call 911 immediately.