Module 5. Medical Emergencies
Allergic Reactions
Most allergies are mild, but some can be life-threatening. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
Common Triggers of Anaphylaxis
- Peanuts and tree nuts
- Shellfish and dairy
- Insect stings (bees, wasps)
- Certain medications (penicillin, NSAIDs)
Signs of an Allergic Reaction
×
Signs of an Allergic Reaction
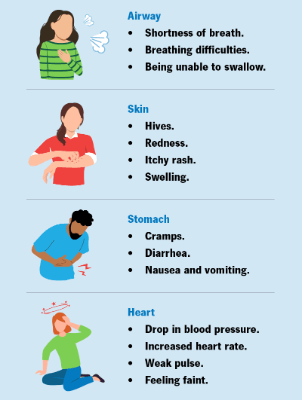 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved

Mild Symptoms:
- Itchy skin, rash, or hives
- Sneezing or watery eyes
Severe Symptoms (Anaphylaxis):
- Swelling of the face, tongue, or throat
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Rapid or weak pulse
- Dizziness or fainting
- Nausea or vomiting
What to Do in an Allergy Emergency
Step 1: Ask About an EpiPen
If the person carries an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen), help them use it.
-
Using EpiPen
×Using EpiPen
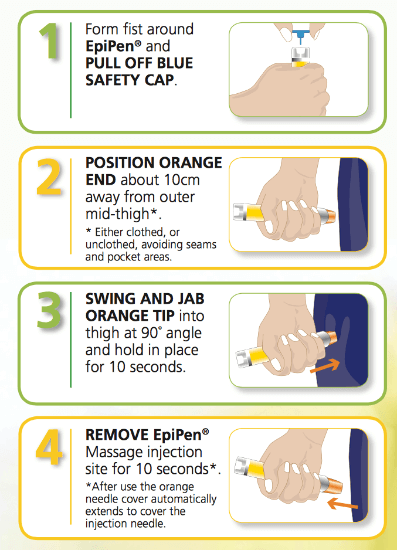 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved- Remove the safety cap.
- Hold it like a fist, orange tip pointing downward.
- Press firmly into the outer thigh (through clothing if necessary).
- Listen for a click—this means the medication is injected.
- Hold in place for 3 seconds, then remove.
- Massage the area for 10 seconds.
Step 2: Call 911 Immediately
Even if the person feels better after using the EpiPen, they still need medical attention. The reaction can return and may require a second dose.
Step 3: Keep the Person Calm & Monitor Their Condition
- Have them sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
- Watch for worsening symptoms.
- Be prepared to begin CPR if they stop breathing.
No EpiPen available? Call 911 and stay with the person.
Key Takeaways
- Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction.
- Common triggers include nuts, shellfish, insect stings, and medications.
- Use an EpiPen immediately if available, then call 911.
- Always monitor the person—symptoms can return.
Are All Bites Dangerous?
Most animal bites are minor, but some can lead to serious infections or even rabies. Human bites, surprisingly, can be even more dangerous due to the number of bacteria in our mouths.
When to Seek Emergency Care
- A bite from an undomesticated, wild animal (raccoon, bat, fox, skunk, coyote) – Rabies risk!
- A deep or puncture wound – High risk of infection
- A bite on the face, hands, or joints – These areas are prone to complications
- Swelling, redness, pus, or fever – Signs of an infection
If Bitten by a Wild or Unprovoked Animal
- Control bleeding – Use a clean cloth to apply firm pressure.
- Clean the wound thoroughly – Wash with warm water and anti-bacterial soap for at least 5 minutes.
- Apply antibiotic ointment – Neosporin or a similar antiseptic helps prevent infection.
- Cover with a sterile bandage – Change it frequently to keep the wound clean.
- Seek medical care immediately – A rabies shot may be necessary.
Rabies Facts
- Rabies is almost always fatal if symptoms appear.
- The rabies vaccine is effective only if given early after exposure.
- Bats, raccoons, skunks, foxes, and coyotes are the most common carriers.
If Bitten by a Domestic Pet (Dog or Cat)
Most domestic pet bites are not serious, but they can still cause infection. If the pet is vaccinated and shows no signs of rabies, monitor the wound and apply basic First Aid.
- Wash the area with soap and water.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment (like Neosporin).
- Cover with a clean bandage and change it daily.
See a doctor if:
- The pet was behaving aggressively or is not up-to-date on rabies shots.
- The bite gets red, swollen, or painful after a day or two.
Human Bites: More Dangerous Than You Think
Believe it or not, human bites carry more bacteria than most animal bites and can lead to serious infections.
- Wash the area thoroughly with soap and water.
- Apply an antiseptic or antibiotic ointment.
- Cover with a sterile bandage.
- Monitor for signs of infection (redness, swelling, pus, fever).
See a doctor if:
- The bite is deep or bleeding heavily.
- There are signs of infection.
- The bite is near a joint, as infections can spread to the bones.
Key Takeaways
- Wild animal bites can lead to rabies, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Human bites often cause severe infections and may need antibiotics.
- Always wash the bite wound thoroughly with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Monitor for signs of infection—swelling, redness, pus, or fever mean you should see a doctor.
What is an
Asthma Attack
×
Asthma Attack
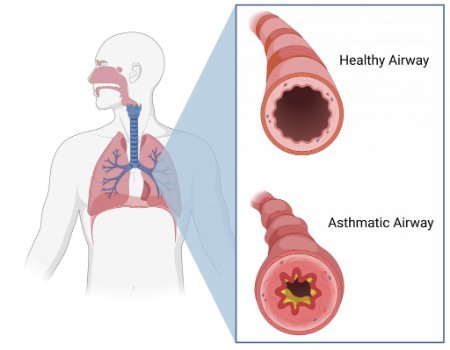 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
?

An asthma attack occurs when the airways become inflamed, swollen, and narrowed, making it difficult to breathe. Without treatment, an asthma attack can be life-threatening.
Asthma attacks can come on suddenly and range from mild to severe. Quick treatment is essential!
Causes & Triggers of Asthma Attacks
- Allergens (pollen, dust, pet dander, mold)
- Cold air or weather changes
- Exercise (especially in dry air)
- Smoke or strong odors (perfume, chemicals, pollution)
- Respiratory infections (cold, flu, bronchitis)
- Stress or anxiety
Signs & Symptoms of an Asthma Attack
×
Signs & Symptoms of an Asthma Attack
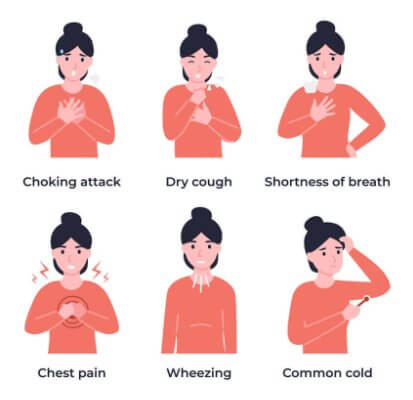 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved

- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Wheezing (whistling sound when breathing out)
- Tightness or pressure in the chest
- Coughing (especially at night or early morning)
- Pale or bluish lips, fingertips, or face (severe cases)
If breathing becomes extremely difficult, call 911 immediately.
First Aid for an Asthma Attack
Step 1: Stay Calm & Help the Person Stay Calm
- Panic can worsen breathing difficulties.
- Encourage slow, steady breaths.
Step 2: Help Them Use Their Inhaler
- Most asthma inhalers contain a bronchodilator (like albuterol) to open the airways.
- Shake the inhaler well.
- Have the person exhale completely.
- Place the inhaler mouthpiece between the lips (or use a spacer if available).
- Have them inhale deeply while pressing the inhaler.
- Hold the breath for 10 seconds, then exhale slowly.
- Repeat if needed, as directed by their asthma action plan.
Step 3: Move the Person to a Safer Environment
- Get them away from smoke, strong odors, or allergens.
- Have them sit upright to make breathing easier.
Step 4: Call 911 if the Attack Worsens
- If the person’s breathing does not improve after using their inhaler, call for emergency help.
- If they are too weak to speak, are gasping for air, or turn blue, call 911 immediately.
Even if symptoms improve, follow up with a doctor. Asthma attacks can return if left untreated.
When to Call 911
- The inhaler does NOT help after multiple uses.
- The person cannot speak more than a few words at a time.
- Breathing is getting worse or they appear extremely weak.
- Lips, fingernails, or face turn blue (sign of oxygen deprivation).
- The person becomes unresponsive—start CPR if they stop breathing.
Severe asthma attacks can be fatal—do not delay emergency care!
Key Takeaways
- An asthma attack causes airway swelling and difficulty breathing.
- Common triggers include allergens, smoke, stress, and cold air.
- Help the person use their inhaler properly and keep them calm.
- Call 911 if their breathing does not improve or worsens.
What is Fainting?
Fainting (syncope) is a temporary loss of consciousness due to reduced blood flow to the brain. It usually lasts less than a minute, and the person regains consciousness quickly. Fainting is often preceded by warning signs like:- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Weakness or blurred vision
- Sudden sweating or nausea
First Aid for Fainting
- If someone feels dizzy and may faint, help them to the ground safely—support them to prevent injury.
- Have them lie down and elevate their legs to improve circulation.
- If they do not improve or symptoms worsen, call 911.
- If someone faints and does not wake up immediately, call 911 and check for breathing.
- Be prepared to start CPR if they become unresponsive.
Blood Sugar Emergencies: High vs. Low
Fainting can also be caused by blood sugar imbalances, especially in people with diabetes.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
×
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
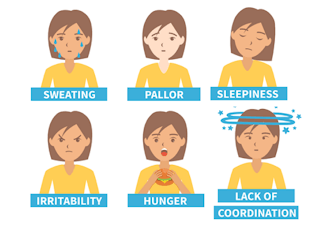 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
Cause: Skipping meals, too much insulin, excessive exercise, or certain medications.

- Extreme lethargy or weakness
- Confusion or irritability
- Drowsiness or sweating
- Excessive thirst
- Give them something sugary to drink—fruit juice, cola, or glucose tablets.
- If they don’t improve within 10 minutes, call 911.
- Do not give food or drink if they are unconscious.
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
×
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
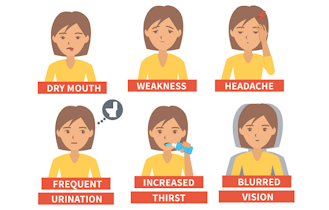 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
Cause: Poor diet, lack of insulin, stress, or illness.

- Extreme thirst
- Frequent urination
- Dry skin, nausea, or confusion
- Encourage the person to drink water.
- If they show signs of confusion, weakness, or vomiting, call 911 immediately.
When to Call 911
- The person remains unconscious after fainting.
- They have trouble breathing or chest pain.
- Symptoms do not improve within 10 minutes after giving sugar for low blood sugar.
- They are confused or disoriented—this could signal a diabetic emergency.
Key Takeaways
- Fainting is usually brief but may signal an underlying problem.
- Help a fainting person lie down with legs elevated to restore circulation.
- Diabetic emergencies can cause fainting due to high or low blood sugar.
- Give sugary drinks for low blood sugar, but call 911 if symptoms don’t improve.
Understanding Nosebleeds
A nosebleed occurs when the fragile blood vessels inside the nose break, leading to bleeding. While nosebleeds are usually harmless, they can be alarming. Most stop on their own with proper First Aid.
Common Causes of Nosebleeds
×
Common Causes of Nosebleeds
 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved

- Trauma – a fall, hit to the nose, or excessive nose-picking
- Dry air – low humidity can dry out and crack nasal tissues
- Allergies & colds – irritated nasal passages increase the risk
- High blood pressure – can contribute to frequent nosebleeds
First Aid for Nosebleeds
What NOT to Do
- Do not tilt the head backward—this can cause blood to drain into the throat and stomach, leading to choking or nausea.
- Do not lie down—this may increase blood flow.
- Do not stuff tissues or cotton into the nose—this can make it worse.
What to Do Instead
×
What to Do Instead
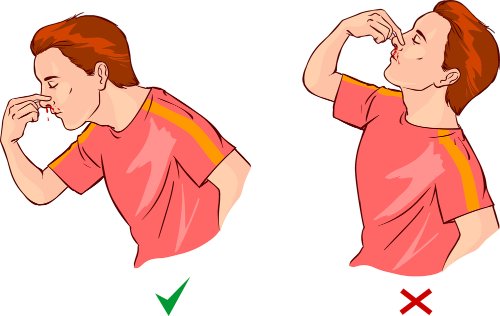 © FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved
© FAW Training Solutions – All rights reserved

- Have the person sit upright—this reduces blood flow to the nose.
- Loosen tight clothing around the neck.
- Have them spit out excess saliva to prevent nausea.
- Pinch the nostrils shut and press the tip of the nose against the bony part of the face.
- Maintain pressure for 5 to 10 minutes without releasing.
- Once bleeding stops, avoid nose-blowing or straining for at least an hour.
When to Call 911
- The nosebleed lasts longer than 15–20 minutes.
- The person loses a significant amount of blood.
- The bleeding occurs after a head injury or a broken nose.
- The person has trouble breathing or is coughing up blood.
Key Takeaways
- Most nosebleeds are minor and stop on their own with proper First Aid.
- Sit upright, pinch the nostrils shut, and apply pressure for 5–10 minutes.
- Do not tilt the head backward, lie down, or stuff tissues into the nose.
- Call 911 if the bleeding lasts over 15 minutes or follows a head injury.